By Shahneel Ahmed Ovaries are reproductive glands found only in females. The ovaries produce eggs, which travel through the fallopian tubes and into the uterus where the fertilized egg implants and develops into a fetus. In addition, the ovaries are the main source of the female hormones estrogen an...
By Shahneel Ahmed
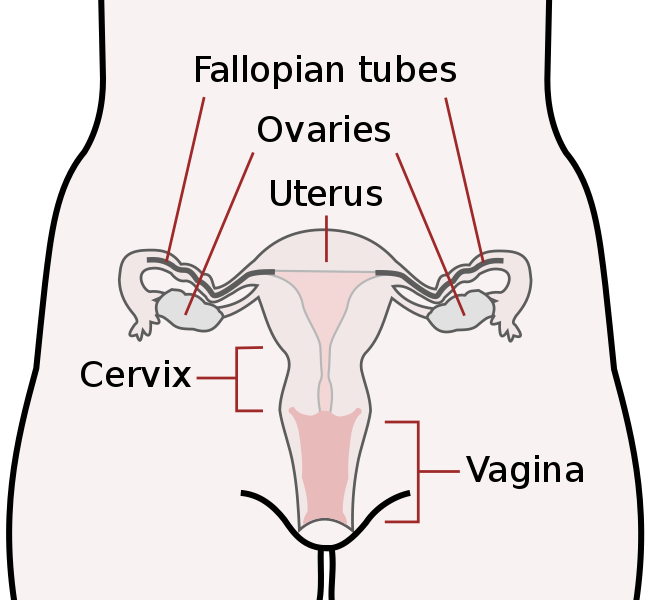
Ovaries are reproductive glands found only in females. The ovaries produce eggs, which travel through the fallopian tubes and into the uterus where the fertilized egg implants and develops into a fetus. In addition, the ovaries are the main source of the female hormones estrogen and progesterone. There is one ovary on each side of the uterus. One ovary is about the size of an almond.
Cancer starts when cells in the body begin to grow uncontrollably. Ovarian cancer was previously believed to begin only in the ovaries. However, recent findings show that it may start at the tail ends of the fallopian tubes. Early stage ovarian cancer rarely causes any symptoms.
Only about 20% of ovarian cancers are found at an early stage. When ovarian cancer is found in the early stages, about 94% of patients live longer than five years after diagnosis. According to the American Cancer Society, prompt attention to symptoms may improve the odds of early diagnosis and successful treatment. If you have symptoms similar to those of ovarian cancer almost daily for more than a few weeks or more than 12 times during the course of one month, report them right away to your health care professional.
There is a lot of research to develop a screening test for ovarian cancer. The two tests used most often are a transvaginal ultrasound and the CA-125 blood test. A transvaginal ultrasound uses sound waves to look at the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries. It can help find a mass in the ovary, but it is unable to tell if the mass is cancerous or benign. CA-125 is a protein in the blood, and the CA-125 blood test measures the amount of this protein. Women with ovarian cancer have high levels of CA-125. Better ways to screen for ovarian cancer are still being researched.
The most common symptoms of ovarian cancer include bloating, pelvic or abdominal pain, trouble eating or feeling full quickly, and urinary urgency or frequency. These symptoms are also caused by other conditions. In fact, most of these symptoms occur just about as often in women who do not have ovarian cancer. When these symptoms are caused by ovarian cancer, they are persistent and occur more often and/or severe than normal. Other symptoms include fatigue, upset stomach, back pain, painful sex, constipation, menstrual changes, abdominal swelling, and weight loss.
Risk factors for ovarian cancer include older age, inherited gene mutations (BRCA1 and BRCA2), family history of ovarian cancer, estrogen hormone replacement therapy, beginning menstruation at an early age, and starting menopause at a later age. Treatment of ovarian cancer usually involves surgery and chemotherapy. If you should be experiencing any of these symptoms more than your regular menstrual cycle duration, contact your primary physician or gynecologist and book an appointment to have yourself examined. Being diagnosed early might just save your life.